How the Taycan Recovers Energy While Driving
Minus to plus: The recuperation system feeds some of the braking energy back into the battery of the Taycan and is responsible for one-third of the vehicle’s range.
The autobahn is empty and you’re driving 200 kmh, until a small delivery van changes lanes to pass a truck. No problem – you’re maintaining a safe distance and slow down to 100 kmh. But a great deal of energy is consumed in the blink of an eye, as vehicles with an internal combustion engine convert kinetic energy into heat when the brakes are applied, which they’re unable to use. Electric vehicles, on the other hand, can recover a large portion of this energy, using the electric machines as generators when slowing down and storing the power generated in the battery. For example, the Porsche Taycan can use a significant amount of the braking energy for propulsion, which is referred to as recuperation, based on the Latin recuperare. Recuperation has established itself as a technical term. Kinetic braking energy increases twice as fast as speed – double the speed means four times the recuperation. When braking from 100 kmh, the Taycan generates four times as much energy as when braking from 50 kmh. This recuperation and the propulsion itself both play a key role in the efficiency of electric vehicles.
How does the Taycan do that?
“We incorporate the electric motors we produce in Zuffenhausen into the brake system for the purpose of energy recovery,” explains Ingo Albers, Head of Chassis Development at the Porsche development center in Weissach. “Electric motors can generally be controlled in four-quadrant operation.” In other words, an electric motor can work with both the rotation speed and torque running in the same – positive – direction. But each electric motor can also function as a generator, in which case the motor continues to turn in the same direction, but is now powered by the wheels rather than powering them itself. It generates electrical energy, rather than consuming it. And because it takes a lot of energy to power the motor and thus turn the rotor against the magnetic resistance, this negative torque can be used to brake the vehicle.
Double the power:
The two electric motors at the front and rear axles of the Taycan are incorporated into the brake system.The control units and power electronics of the electric motors in the Taycan are therefore intelligently connected with the controls and logics of the brake control system. The conventional hydraulic wheel brake and electric motors can slow down the vehicle together. The experts in Weissach have developed a complex recuperation strategy. Within milliseconds, the electronics decide what percentage of the braking will be electric and what percentage will be hydraulic. While the driver cannot feel the difference, they can see it in the power meter in the instrument cluster.
“We plan to further increase the efficiency of recuperation.”
Ingo Albers
Around 90 percent of everyday braking is 100 percent electric, allowing the Taycan to recover energy. “But in extreme situations, such as full braking from a top speed in a fully loaded Taycan, a maximum braking capacity of more than two megawatts must be applied,” says Albers. “The electric powertrain cannot do that alone. The conventional wheel brake is then applied to a higher degree.” It may also activate because the battery is already full and can no longer recharge through recuperation. Just in case – take, for instance, downhill driving – the hydraulic wheel brake is designed for high performance. Thanks to the design of the electric motors and the electronics in conjunction with Porsche’s signature intelligent control, the Taycan can recuperate with up to 290 kilowatts. “That’s at the absolute top of the field,” says Albers. “And we plan to increase this value.”
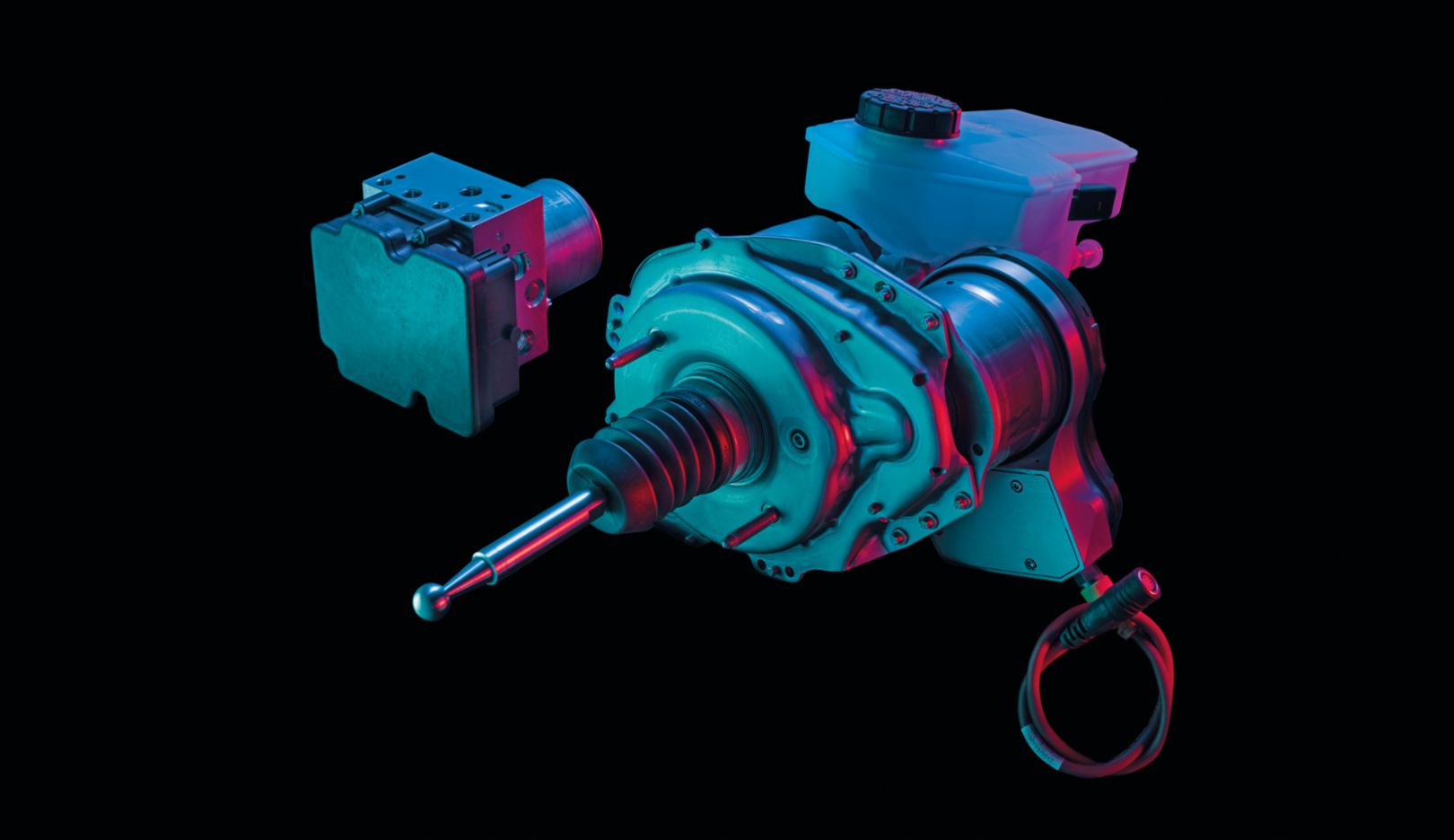

Coordinating recuperation:
In combination with the electromechanical brake booster, Porsche Stability Management (PSM) ensures that the Taycan always maintains the same pressure point in the brake pedal.Following our own path
Some car manufacturers have the electric drive’s recuperation system activate automatically the moment the driver removes their foot from the gas pedal, which is referred to as one-pedal driving. “We made the decision to go a different route with the Taycan,” says Albers. “You apply the brakes to slow down, which is a learned behavior and it’s authentic. The driver receives consistent, predictable feedback. We also offer full integration of systems such as ABS and PSM.” Technically speaking, it would be much easier to apply the electric motor braking to the gas pedal, rather than integrating it into the brake system. “But we incorporated limited recuperation into the gas pedal, which the driver perceives to be efficient, smooth coasting particularly in rural areas,” explains Ingo Albers.
In other words, Porsche will always be Porsche – in continuous optimization. We even defined our own path when developing the first all-electric sports car in Zuffenhausen – always with the goal of maximum efficiency. With this clever strategy in the background, the Taycan secures around one-third of its range with the recovery of brake energy, i.e. recuperation.






